Warehouse pallet racks should conform to certain criteria, indicated by an IPPC, International Plant Protection Convention, stamp with certain letters signifying wood treatment measures taken.
The IPPC was created by the Food and Agriculture Organization, to protect against infestation, especially when shipping food products.
These markings have been developed, per the International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (ISPM) 15.
Its mission is to protect the plant populations world-wide from the destructive effects of invasive species
What is an IPPC logo?
The IPPC logo certifies that the wood used on its pallets was heat-treated as required by the American Lumber Standard Committee (ALSC). Currently, pallet manufacturers requiring a compliant IPPC heat- treated logo, resort to coding methods that are labor intensive and unreliable.
Who founded IPPC?
The IPPC was created by member countries of the Food and Agriculture Organization. The IPPC places emphasis on three core areas: international standard setting, information exchange and capacity development for the implementation of the IPPC and associated international phytosanitary standards.
Why was IPPC formed?
The International Plant Protection Convention (IPPC) is an international plant health agreement, established in 1952, that aims to protect cultivated and wild plants by preventing the introduction and spread of pests.
What is an IPPC permit?
In essence, the IPPC Directive is about minimizing pollution from various industrial sources throughout the European Union. Operators of industrial installations operating activities covered by Annex I of the IPPC Directive are required to obtain an environmental permit from the authorities in the EU countries.
Source: https://www.srs-i.com/blogs/ippc-pallet-markings-meaning/
What Does ISPM 15 Do?
ISPM 15 outlines a set of regulations designed to minimize the spread of diseases and pests from one country to another. While not an international law per se, many countries have agreed to adopt the regulations, including the United States, Australia, and the UK.
Pests and biological infections can spread through wood used in packaging materials, including pallets, crates, dunnage, and more.
What Happens if the Pallet Has no Markings?
Without markings, when shipping internationally, a country may not accept the pallet. Sometimes customs may fumigate the pallet and charge the supplier a premium for doing so.
What Are the Standards?
ISPM 15 requires heat treatment for 30 minutes at 56 degrees Celsius for all wood-based packaging material. Alternatively, the shipper or shipping company can fumigate the wood with Methyl Bromide.
Who Certifies the Wood and Applies the Markings?
The entity that applies the IPPC certification marking must be licensed and meet specific standards under ISPM 15. The wood must also be debarked before treatment.
Why Must You Debark the Wood?
Debarking the wood, removing the bark prevents bugs or worms from re-infesting the wood.
Do These Regulations Pertain to All Wood?
ISPM 15 standards, due to the extremely low risk of infestation, exempts some wood.
This includes sawdust, heat-treated barrels containing wine or spirits, wooden veneer gift boxes, wood packaging less than 6 mm thick, and veneer peeler cores (thin strips of wood peeled from log cores leftover from sawmill operations).
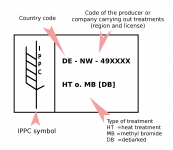
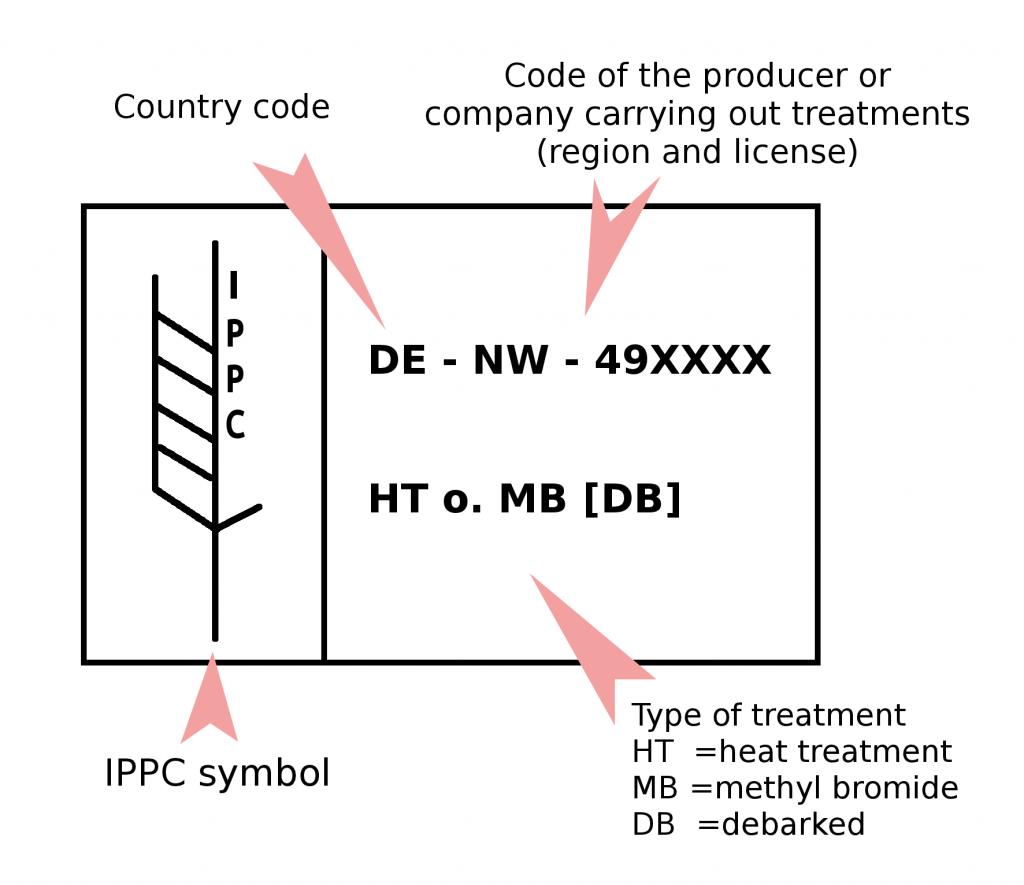
What Does the Mark Look Like?
The mark is a stencil or brand, usually with the IPPC symbol, a country code along with the manufacturer’s registration code, and treatment codes.
The treatment company must clearly mark the wood on two opposite sides.
Can You Reuse Treated Pallets?
If the pallet remains intact and you do not remove any components from it, you can reuse the pallet for shipping. However, if you need to repair it, a certified IPPC fumigator or heat-treatment company must re-treat the wood.
What Are the Codes Used?
A two-digit code, such as “US” for the United States, indicates the county. Each licensed fumigating and heat-treating plant has a unique number code.
There are four treatment codes:
HT – Heat treated.
MB – Methyl Bromide fumigation used.
KD – Kiln Dried, a type of heat treatment to minimize moisture content in the wood.
DB – Debarked, certifying the bark has been removed.
Why Are Some Pallets Heat-Treated and Others Fumigated?
Heat treatment not only kills pests or bacteria and fungi; it prolongs the life and safety of pallets by removing moisture and slowing decay.
If a pallet is heat treated instead of fumigated with Methyl Bromide, it is safe for Do-It-Yourself projects, kindling, or other uses outside of shipping.
Many countries today, including European Union members, prohibit the use of Methyl Bromide as it has been linked to Ozone depletion in the atmosphere. Some Asian countries still use Methyl Bromide to fumigate pallets.
Is Methyl Bromide Toxic?
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) considers Methyl Bromide extremely toxic. Most countries, including the United States, stopped using Methyl Bromide on pallets since 2005.
Inhaling Methyl Bromide fumes can cause vomiting, dizziness, convulsions, and hallucinations. Skin contact with the chemical can result in blisters, redness, and pain.