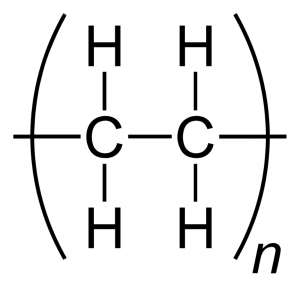
What is Polyethylene?
This thermoplastic polymer is chemically synthesized from ethylene, which comes from petroleum or natural gas. Various plasticizers are used to make polyethylene as well, as the extra substances will enhance the durability and other advantages of the plastic. Above all, polyethylene is refreshingly versatile, which is the best distinguishing factor of the plastic yet!
Remember our recent post on that special type of plastic, polypropylene? Well, we have a new term for you this week- polyethylene (PE). Although the two may sound similar, polypropylene and polyethylene are actually quite different.
Polyethylene. The name sounds strange, but what is it? The most common type of plastic. You see it and touch it every single day, whether you realize it or not. Each year, about 80 tons of polyethylene is produced all around the world.
How is Polyethylene Made?
Low-density polyethylene is created using oxygen as its catalyst, while high-density polyethylene is created by applying more pressure to the ethylene molecules. Lower-density polyethylene is able to be stretched easily, while higher-density polyethylene is more solid.
When was Polyethylene Discovered?
It all goes back to 1898 when polyethylene was produced by mistake by a German chemist, Hans von Pechmann. He was studying a chemical compound called diazomethane when the waxy, whitish plastic was synthesized. He was so intrigued by his scientific blunder over his actual diazomethane experiment that he turned his focus over to researching polyethylene.
It took until 1933 for polyethylene to become an actual industrial manufacturing practice. By witty coincidence, manufacturing polyethylene was also stemmed accidentally by Eric Fawcett and Reginald Gibson. The chemists applied extremely high pressure to a mixture of ethylene and benzaldehyde which produced polyethylene. Like Pechmann, Fawcett and Gibson were shocked and intrigued by the white, waxy substance that they were not expecting to synthesize.
What is Polyethylene Used For?
- Plastic grocery bags
- Shopping bags
- Sandwich bags
- Plastic wrap
- Shampoo bottles
- Milk containers
- Toys
- Garbage bags
- Tupperware
- Bullet-proof vests
- Knee joint replacements
- Gas pipes
- Plastic bottles
- Films and foam
- Medicine containers
- Insulation in electrical wiring
What are the benefits of Polyethylene?
- Can be melted into a liquid and remolded to a solid-state
- Soft, yet durable
- Flexible
- Pliable
- Safe to use in various types of environments
- Can be customized and colored
- Shatter-resistant
How Does Polyethylene Differ From Polypropylene?
- Polyethylene is more translucent and creates a lower static charge, making it ideal for storage.
- Polyethylene’s lower static charge means it attracts less dust and dirt.
- Polyethylene is more flexible than polypropylene.
- Polyethylene is known as the father of polypropylene because the plastic itself is purer.
- Polyethylene is less likely to tear than polypropylene.
- Polyethylene costs more than polypropylene, however, is superior.